Let me guess—you’re trying to understand industrial automation systems and integration without falling asleep halfway through. Same. I’ve spent enough time around factories, control panels, and dashboards to know one thing: automation is powerful, but people explain it in the most painful way possible.
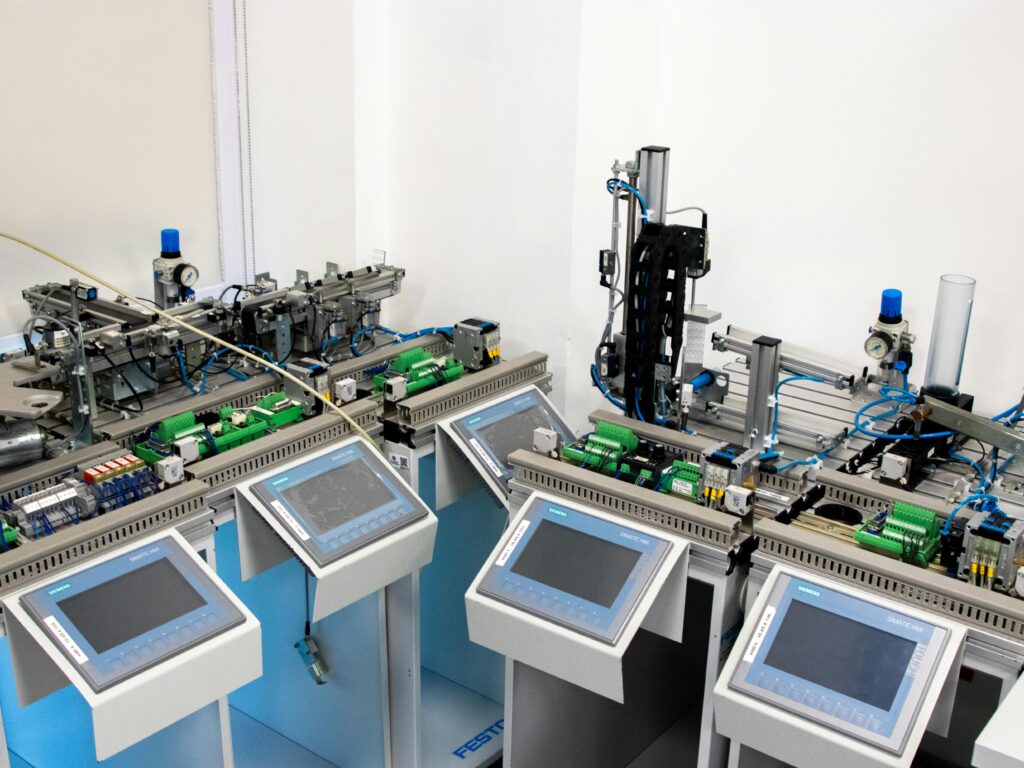

So let’s fix that. I’ll walk you through what industrial automation really is, how integration fits into the picture, and why it matters so much—using plain language, real opinions, and zero robotic vibes. Sound good?
What Industrial Automation Actually Means
Industrial automation simply means using machines, software, and control systems to handle tasks with minimal human intervention. Instead of someone flipping switches all day, systems make decisions automatically. Simple, right?
I like to think of it as putting your factory on autopilot—but with way more sensors and fewer snacks. Automation handles repetitive work faster, safer, and more accurately than humans ever could. And yes, it does it without complaining.
Read more about Automate and integrate smart home devices.
Core Pieces of Industrial Automation Systems

You’ll usually see these components working together:
- PLCs (Programmable Logic Controllers) for control logic
- Sensors and actuators to read and act on real-world conditions
- HMIs (Human-Machine Interfaces) for operators to interact with systems
- SCADA systems for monitoring and control
- Industrial networks to keep everything talking
Each piece plays a role, and integration makes sure they don’t act like strangers at a party.
Why Integration Is the Real MVP
Automation alone helps, but integration makes it powerful. Integration connects machines, systems, and software so they work as one smooth operation instead of isolated islands.
Ever seen a factory where one machine finishes its job, but the next one has no idea? Yeah, that’s what happens without integration. IMO, that’s wasted potential.
What Industrial System Integration Does
Integration allows systems to:
- Share real-time data
- Coordinate actions automatically
- Reduce downtime
- Improve decision-making
FYI, companies that integrate their automation systems almost always see faster production cycles and fewer headaches. Coincidence? Not even close.
Types of Industrial Automation Systems
Not all automation looks the same. Different industries use different levels depending on complexity and budget.
Fixed Automation
This setup handles one task repeatedly. Think assembly lines.
- High production speed
- Low flexibility
- Expensive to change
Great for mass production, terrible if you like variety.
Programmable Automation
This system allows reprogramming for different tasks.
- Flexible production
- Lower speed than fixed automation
- Popular in batch manufacturing
I’ve worked around programmable systems, and honestly, the flexibility saves the day more often than you’d expect.
Flexible Automation
This is the fancy stuff.
- Handles multiple products
- Minimal changeover time
- Higher initial cost
Companies love flexible automation when customer demand keeps changing. And let’s be real—demand always changes.
Key Technologies Driving Automation and Integration
Industrial automation systems don’t run on magic. They rely on some very specific tech.
PLCs and PACs
PLCs handle control logic, while PACs (Programmable Automation Controllers) handle more complex tasks. I’ve always preferred PACs for data-heavy environments—they feel less restrictive.
Industrial IoT (IIoT)
IIoT connects machines to networks and analytics platforms.
- Real-time monitoring
- Predictive maintenance
- Smarter decision-making
Ever wondered how factories predict failures before they happen? IIoT does the heavy lifting.
SCADA and MES Systems
SCADA monitors operations, while MES (Manufacturing Execution Systems) manage production workflows. When you integrate these two, things get very efficient.
Benefits of Industrial Automation Systems and Integration
This is where things get exciting.
Increased Efficiency
Automation speeds up processes and reduces errors. Integration ensures every system moves in sync. Less waiting, more producing.
Improved Product Quality
Machines repeat tasks consistently. Integrated systems catch defects early. Humans get tired—machines don’t.
Better Safety
Automation keeps people away from dangerous tasks. I’ve seen workplaces transform safety records just by automating high-risk processes.
Cost Savings Over Time
Yes, automation costs money upfront. But long-term savings from reduced waste, downtime, and labor costs make it worth it.
Bottom line: automation pays off if you integrate it properly.
Real-World Example (Because Theory Is Boring)
I once saw a manufacturing plant automate packaging but skip integration with inventory systems. Result? Machines worked fast, but inventory data lagged behind. Chaos followed.
Once they integrated automation with ERP and inventory software, everything clicked:
- Accurate stock levels
- Faster order fulfillment
- Fewer late-night panic calls
Moral of the story? Automation without integration only solves half the problem.
Common Challenges (Yes, They Exist)
Let’s not pretend it’s all sunshine.
Compatibility Issues
Different vendors don’t always play nice. Integration fixes this, but it takes planning.
Cybersecurity Risks
Connected systems attract attention. Secure networks and access control matter—a lot.
Skill Gaps
Automation systems need skilled people. Training teams matters just as much as buying hardware.
Still, these challenges don’t outweigh the benefits. They just mean you need a smart plan.
Best Practices for Successful Integration
If you want industrial automation systems and integration to actually work, follow these rules:
- Plan before you buy
- Choose open communication standards
- Integrate step by step
- Document everything
- Train your team early
I’ve seen rushed automation projects fail badly. Taking your time saves money and sanity.
Automation vs Manual Processes (Quick Comparison)
Let’s be honest—manual systems still exist, but automation wins most rounds.
Automation systems offer:
- Faster production
- Higher accuracy
- Real-time data
- Scalability
Manual systems offer:
- Lower upfront cost
- Flexibility for very small operations
Once production grows, automation becomes unavoidable.
The Future of Industrial Automation and Integration
Automation keeps getting smarter. AI, machine learning, and advanced analytics already shape modern factories. Integrated systems don’t just react—they predict and optimize.
Factories now move toward:
- Self-optimizing production
- Predictive maintenance
- Fully connected ecosystems
Sounds futuristic, but it’s already happening. Wild, right?
Final Thoughts: Why This Stuff Matters
Industrial automation systems and integration aren’t optional anymore. They drive efficiency, safety, and competitiveness across industries. Automation handles the work, and integration makes everything work together.
If you take one thing from this article, let it be this: automation works best when systems communicate, share data, and act as one. Anything less leaves performance on the table.
So whether you’re planning a factory upgrade or just curious about how modern industry runs, keep your eye on automation—and never ignore integration. Trust me, future-you will thank you. Learn more here Time Tracking Tools Free: Real Tools That Actually Help You Get More Done